Understanding Customer Segmentation sets the stage for businesses to thrive by customizing marketing approaches for different customer groups. Get ready to dive into a world where data drives decisions and success knows no bounds.
Let’s explore the various facets of customer segmentation and how it can revolutionize the way companies connect with their audience.
Importance of Customer Segmentation
Understanding customer segmentation is like the key to the city for businesses. It’s all about dividing your customers into groups based on similar characteristics or behaviors. This allows companies to tailor their marketing strategies to meet the specific needs and preferences of each segment. In a world where one size definitely does not fit all, customer segmentation helps businesses reach the right people with the right message at the right time.
Tailoring Marketing Strategies
Customer segmentation is the secret sauce that helps businesses create targeted marketing campaigns. By identifying different customer segments, companies can personalize their messaging, product offerings, and promotions to resonate with each group. For example, a clothing retailer might use customer segmentation to offer different styles to different age groups or preferences. This level of personalization can lead to higher customer satisfaction, increased loyalty, and ultimately, more sales.
Examples of Successful Companies
Companies like Amazon and Netflix are prime examples of businesses that have mastered the art of customer segmentation. Amazon uses data from customer purchases and browsing behavior to recommend products tailored to individual preferences. Netflix analyzes viewing habits to suggest personalized movie and TV show recommendations. By leveraging customer segmentation, these companies have created highly targeted marketing strategies that keep customers coming back for more.
Types of Customer Segmentation

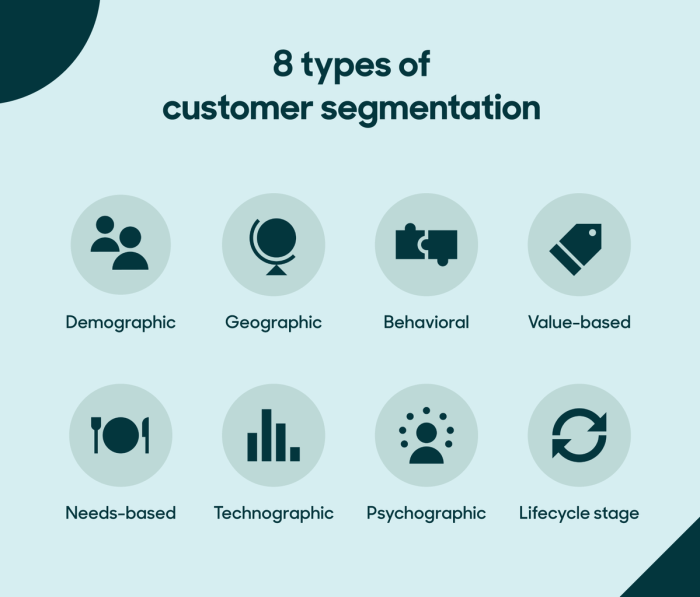
When it comes to understanding customer segmentation, there are several common types that businesses use to categorize their target audience. These include demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral segmentation.
Demographic Segmentation
- Demographic segmentation involves categorizing customers based on factors such as age, gender, income, education, occupation, and family size.
- For example, a company selling luxury skincare products may target women aged 30-50 with a household income above $100,000.
- Advantages: Easy to obtain data, widely used, helps in creating targeted marketing campaigns.
- Disadvantages: Oversimplification of customer behavior, may not capture individual preferences.
Geographic Segmentation, Understanding Customer Segmentation
- Geographic segmentation divides customers based on their location, such as country, region, city, or climate.
- For instance, a fast-food chain may offer different menu items based on regional preferences, like spicy food in the South.
- Advantages: Helps in localizing marketing efforts, considers cultural differences, targets specific regions effectively.
- Disadvantages: Ignores individual differences within the same geographical area, may limit market potential.
Psychographic Segmentation
- Psychographic segmentation focuses on customers’ lifestyles, values, interests, attitudes, and personality traits.
- For example, a fitness brand may target health-conscious individuals who value sustainability and outdoor activities.
- Advantages: Provides insights into customer motivations, helps in creating emotional connections, targets niche markets effectively.
- Disadvantages: Requires in-depth research, may be subjective, difficult to quantify.
Behavioral Segmentation
- Behavioral segmentation categorizes customers based on their purchasing behavior, such as loyalty, usage rate, buying occasion, or benefits sought.
- For instance, a coffee chain may offer loyalty rewards to frequent customers to increase retention.
- Advantages: Reflects actual customer actions, helps in predicting future behavior, allows for personalized marketing strategies.
- Disadvantages: Relies on past behavior, may not consider changing preferences, requires continuous monitoring.
Data Collection for Customer Segmentation
To effectively segment customers, collecting accurate and relevant data is crucial. Different methods can be utilized for this purpose, such as surveys, interviews, purchase history analysis, and more.
Surveys
Surveys are a common method for collecting data for customer segmentation. By asking targeted questions, businesses can gather valuable insights into customer preferences, behaviors, and demographics.
Interviews
Interviews provide an opportunity for direct interaction with customers, allowing businesses to delve deeper into their needs and motivations. This qualitative data can be instrumental in creating detailed customer segments.
Purchase History Analysis
Analyzing purchase history data can reveal patterns and trends in customer behavior. By understanding past buying habits, businesses can predict future preferences and tailor marketing strategies accordingly.
Importance of Data Accuracy and Relevance
Ensuring data accuracy and relevance is essential for effective customer segmentation. Inaccurate or outdated information can lead to flawed segmentation, resulting in ineffective marketing campaigns and customer outreach.
Best Practices for Ethical Data Collection
Ethical data collection practices are crucial to maintaining customer trust. Businesses should be transparent about the data they collect, obtain consent from customers, and prioritize data security to safeguard sensitive information.
Implementing Customer Segmentation Strategies: Understanding Customer Segmentation
Implementing customer segmentation strategies involves a series of steps to effectively target different customer segments with personalized marketing campaigns and measure the success of these strategies.
Developing Customer Segmentation Strategies
- Identify your target audience: Understand the demographics, behaviors, and preferences of your customers to create meaningful segments.
- Collect and analyze data: Utilize customer data to categorize customers based on similarities and differences.
- Create customer personas: Develop detailed profiles for each segment to better tailor marketing messages and offers.
- Implement personalized campaigns: Use the insights gained from segmentation to deliver targeted messages and promotions to each segment.
Targeting Different Customer Segments
- Customize messaging: Tailor your marketing content to resonate with the specific needs and interests of each segment.
- Utilize multiple channels: Reach different segments through various platforms such as social media, email, and direct mail.
- Offer personalized promotions: Provide discounts, offers, or content that are relevant to the preferences of each segment.
Measuring Success of Customer Segmentation Strategies
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs): Monitor metrics like conversion rates, customer retention, and ROI to assess the impact of segmentation.
- Conduct A/B testing: Compare the performance of segmented campaigns to non-segmented ones to determine the effectiveness of targeting.
- Solicit customer feedback: Gather input from customers to understand their perception of personalized marketing efforts and make adjustments accordingly.